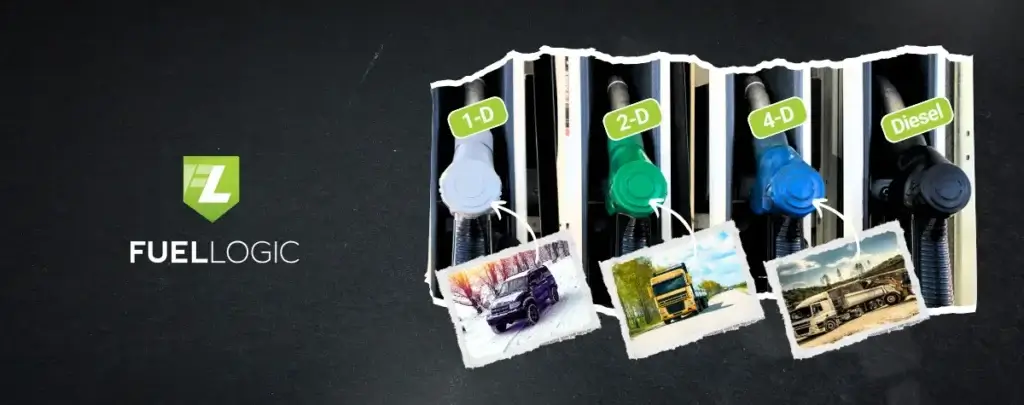
Diesel engines are more efficient than gasoline, achieving over 40% efficiency compared to 20% for gas, making diesel popular among many different types of vehicles due to lower fuel costs. Understanding different types of diesel fuel grades can help you use the right type of diesel fuel.
The quality of diesel fuel can enhance your vehicle’s performance and lifespan. However, not all vehicles require the same type of diesel. Yes, there are different grades of diesel fuel.
This guide reviews each grade based on its impact on engine efficiency, emissions, and reliability. We’ll explain cetane ratings and cloud and pour points. By the end, you’ll know which fuel grade to choose for improved performance and longevity.
What Are Diesel Fuel Grades?
Diesel fuel types are categorized into grades to optimize performance, emissions control, and adaptability to climate.
Governed by ASTM D975 and EPA standards, these grades reflect key factors like cetane rating, sulfur content, and cold weather performance, influencing engine efficiency and environmental impact.
Understanding the differences in diesel fuel grades helps consumers and businesses select the right type of fuel, enhancing performance, reducing emissions, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
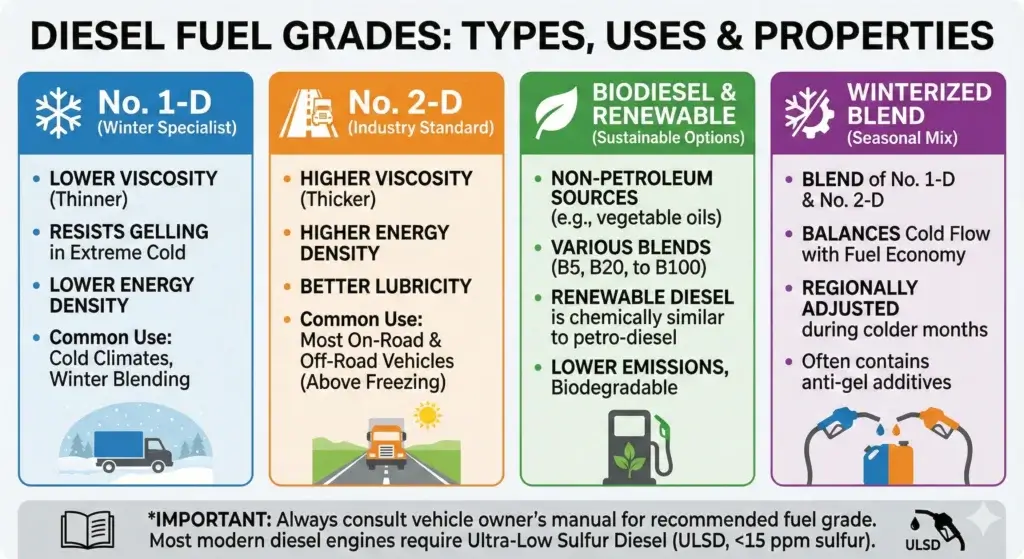
No. 2-D diesel is the most commonly used fuel year-round. In colder climates, No. 1-D diesel or winterized blends are used to prevent gelling and maintain engine performance. Biodiesel and renewable diesel offer cleaner alternatives, with renewable diesel performing most like traditional diesel fuel.
Importance of Understanding Diesel Fuel Grades
Diesel fuel grades are classified by three key factors: cetane rating, cloud point, and pour point. The cetane number indicates how quickly diesel fuel ignites in the engine, while the cloud point is the temperature at which wax crystals form, affecting clarity and flow.
The pour point is the lowest temperature at which diesel fuel remains liquid. These characteristics explain why some types of diesel perform better in cold weather conditions than others. Many fuel types are also blended with additives for specific conditions. Understanding the different types of diesel fuel at the pump—along with their source, composition, and additives—is crucial for optimal fuel performance.
This will help you in selecting the appropriate fuel grade:
- Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD): This type of diesel fuel contains 15 ppm or less sulfur, which means lower emissions, cleaner engine performance, and better fuel economy. It also has good cold-flow properties, making it reliable in winter. ULSD can appear in different grades: 1-D, 2-D, or 4-D.
- Dyed Diesel: Marked with a red dye, this diesel fuel is designed for off-road use and is usually tax-exempt. It’s commonly used in construction equipment, farm machinery, or generators. However, using dyed diesel on public roads is illegal in many areas and can harm certain engines. Most dyed fuel is classified as Grade 2-D or 4-D.
- Biodiesel: Made from renewable sources such as vegetable oil, biodiesel can be blended with standard diesel fuel (1-D, 2-D, or 4-D) to reduce emissions. It improves lubrication and helps reduce engine wear. That said, high concentrations of biodiesel can cause performance issues or compatibility problems with older engines.
- Premium Diesel: Some stations sell “premium” diesel fuel, usually Grade 2-D enhanced with additives. These additives improve fuel economy, help engines run more smoothly, and may extend vehicle life.

Types of Diesel Fuel Grades
There are three main types of diesel fuel: 1-D, 2-D, and 4-D. These diesel grades define performance in various conditions and applications. Here’s a brief overview of each fuel grade:
1. Grade 1-D (Diesel #1)
Grade 1-D (Diesel Fuel #1): This high-quality diesel fuel has low paraffin wax and sulfur content, ensuring easy flow in cold weather. With a cloud point around -40°C, it resists gelling, making it ideal for winter use.
Featuring a cetane rating of 45–55, it enables better cold starts and reduces battery strain. Grade 1-D often includes fuel additives like detergents and rust inhibitors to maintain the fuel system and prevent corrosion. Although it may be pricier due to added lubricants, it enhances fuel efficiency and prolongs engine life.
Its ignition ease and low paraffin wax content make it the right type of diesel for winterized diesel applications.

2. Grade 2-D (Diesel #2)
Grade 2-D (Diesel Fuel #2): This is the most common type of diesel fuel, widely used in trucks, cars, and even diesel generators because of its high energy content and availability. It has lower volatility, higher viscosity, and tends to gel in colder temperatures (around 10°F). The wax it contains, however, provides strong lubrication, which helps extend engine life and cut down on maintenance.
Diesel fuel #2 burns more slowly than #1, making it more fuel-efficient. Like #1, it typically has a cetane rating between 45–55. Its cloud point ranges from -28°C to -7°C, with a higher pour point compared to #1.
In colder regions, many suppliers offer a winterized diesel fuel blend of #1 and #2. This mix provides the lubrication and efficiency of #2 while adding the cold-weather reliability of #1.
To get the best performance, it’s important to source from a reputable diesel fuel supplier that meets industry standards, uses the right additives, and ensures consistent quality testing.
3. Grade 4-D (Diesel #4)
Grade 4-D (Diesel Fuel #4): Sometimes called marine diesel, this grade is a blend of lower-volatility distillates and heavier residual fuel oils. It’s designed for large, low-speed, high-load engines—such as industrial equipment, power plants, or marine vessels.
Because of its thickness, Grade 4-D diesel fuel burns more gradually, allowing for long operation without frequent refueling. It generally has a lower cetane rating and less favorable cold-weather performance compared to #1 or #2, which is why it’s mostly limited to off-road and stationary use.

| Property | Grade 1-D (Diesel #1) | Grade 2-D (Diesel #2) | Grade 4-D (Diesel #4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volatility | High | Lower | Lower |
| Viscosity | Low | Higher | Higher |
| Cloud Point | -40°C | -28°C to -7°C | Higher |
| Pour Point | Low (generally around -40°C) | Higher | Higher |
| Cetane Rating | 45 to 55 | 45 to 55 | Lower (generally not specified) |
| Lubrication | Lower due to lack of wax, more expensive | Good (contains wax) | Good (due to lower volatility) |
| Cold Weather Performance | Excellent, resists gelling | Poor in extreme cold, gelling around 10°F | Poor in cold weather |
| Additives | Detergents, demulsifiers, rust inhibitors | Minimal additives | Lower or minimal additives |
| Engine Application | Commercial trucks, cold climates | General diesel use, year-round | Low-speed engines, off-road equipment |
| Fuel Efficiency | Moderate | High | High, long intervals between refuels |
Key Differences Between Diesel Fuel Grades
Each diesel fuel grade has unique characteristics that affect engine performance, efficiency, and emissions. Below we’ll break down the main differences between diesel fuel #1, #2, and #4—covering composition, additives, efficiency, and common uses.
1. Composition and Additives
- Diesel Fuel #1: A lighter middle distillate, similar to kerosene, with fewer impurities. It contains branched alkanes, cycloalkanes, and aromatics but excludes benzene and most PAHs. Often enhanced with detergents and rust inhibitors to keep engines clean.
- Diesel Fuel #2: Heavier than #1, with a boiling range of 160–360°C (320–680°F). It’s closer in makeup to heating oil and may include PAHs such as phenanthrene and benzo(a)pyrene. Additives are limited—mainly detergents and demulsifiers.
- Diesel Fuel #4: The thickest grade, with higher ash and sulfur levels and sometimes more than 10% PAHs. It usually contains the fewest additives and is intended for heavy-duty or industrial engines.

2. Performance and Efficiency
- Diesel Fuel #1: Excellent for cold-weather starts, smooth operation, and reduced engine wear. Its downside is lower fuel efficiency since it burns faster and has less energy per gallon.
- Diesel Fuel #2: The most balanced grade—higher energy content, slower burn rate, and better fuel economy. Suitable for year-round use in most diesel engines.
- Diesel Fuel #4: Built for endurance. It provides steady power and efficiency in low-speed, high-load equipment, though not ideal for cold-weather performance.
3. Common Uses
- Diesel Fuel #1: Best for cold climates where gelling is a concern. Often used in commercial trucks and vehicles that must start reliably in freezing temperatures.
- Diesel Fuel #2: The everyday choice for most on-road vehicles. Works well in moderate to warm climates and is the most widely available diesel fuel in the U.S.
- Diesel Fuel #4: Reserved for heavy-duty applications—marine vessels, power generators, agricultural machinery, and industrial equipment.

How to Choose the Right Diesel Fuel Grade for Your Fleet?
Picking the right diesel fuel grade is vital for fleet performance, efficiency, and engine longevity. Therefore, consider these key factors when choosing a fuel grade:
1. Engine Type
- Manufacturer Recommendations – Always use the fuel type specified by the engine manufacturer to avoid voiding warranties and damaging the engine.
- Compatibility – Different engines require different fuels. High-performance engines need higher cetane numbers, while older engines can handle lower-quality fuel.
2. Climate and Environmental Factors
- Cold Weather Performance – In cold climates, use a fuel like #1 diesel that won’t gel and make it difficult to start a vehicle.
- Availability – Fuel grade availability varies by region, so consider if the recommended grade is accessible in your area.
- Environmental Regulations – Follow local and national rules on fuel sulfur content, off-road/on-road diesel standards, and emissions.
3. Vehicle Usage and Load
- Light Duty vs Heavy Duty Applications – Light-duty vehicles use lower-sulfur diesel, while heavy-duty trucks and construction equipment may require higher-sulfur diesel or specific blends for optimal performance.
- Impact of Load and Driving Conditions – Vehicle load and driving conditions (city, highway, off-road) influence fuel use and engine performance. Heavier loads and challenging conditions may need fuels with higher cetane or specific additives for better combustion and protection.

Benefits of Using the Correct Diesel Fuel Grade for Fleet
Choosing the right diesel fuel grade goes beyond meeting regulations. It strategically impacts fleet performance, cost-efficiency, and environmental responsibility:
1. Improved Engine Performance
The right fuel grade ensures efficient combustion, maximizing power and torque. It also provides proper ignition which results in smoother running, reducing vibrations and noise. Besides, the correct fuel has a higher cetane number, preventing engine knock, and protecting its components.
2. Enhanced Fuel Efficiency
Better combustion in turn reduces harmful emissions, improving fuel economy. The right fuel grade also optimizes power output while using less fuel.
3. Reduced Maintenance Costs
The correct fuel grade keeps engine parts clean like its filter, reducing deposits and sludge and maintenance costs. Besides, cleaner parts last longer and fewer engine issues mean less vehicle downtime and higher productivity.
4. Better Environmental Performance
Correct fuel grade reduces harmful emissions like particulates and nitrogen oxides. As a result, it contributes to better air quality and meets environmental standards.
Searching for Quality diesel fuel Grade?
Fuel Logic delivers the perfect diesel fuel grade for your fleet—24/7, on-site, and on schedule.
Risks of Using the Wrong Diesel Fuel Grade or Cetane Number

Using the wrong diesel fuel grade can harm your fleet’s performance, reduce engine lifespan, increase emissions, and lead to higher costs and downtime. But these are not the only issues. Many more potential problems may arise such as:
1. Engine Damage
Same as putting gas in a diesel engine that can cause engine damage, using the wrong fuel grade can lead to deposits on engine parts, reducing performance and causing premature wear. In cold weather, high pour point fuel can gel, blocking fuel lines and preventing the engine from starting. Whereas fuel meant for stationary engines, if used in mobile vehicles, can damage the engine due to poor lubrication and inefficient combustion.
2. Reduced Efficiency
An incorrect fuel grade can lead to higher fuel consumption and increased operating costs due to incomplete combustion. It can also reduce engine power, impacting vehicle performance, especially under heavy loads.
3. Emission Problems
Using a fuel grade with a lower cetane number or higher sulfur content can increase harmful emissions and worsen air pollution. This can be problematic in regions with strict environmental regulations, causing your vehicle to fail fuel quality tests and face fines or restrictions.
⚡ Key Takeaways
- Factors like engine type, climate, load, and local regulations should guide your choice of diesel fuel grade for optimal performance and longevity.
- Diesel fuel is divided into grades—#1, #2, and #4—each designed for specific engine types, performance needs, and climate conditions.
- Grade #1 (Diesel #1) performs best in cold weather, while Grade #2 (Diesel #2) is the most common year-round fuel for trucks and commercial vehicles.
- Choosing the right diesel fuel grade improves engine performance, fuel efficiency, and compliance with environmental regulations.
- Using the wrong fuel grade can cause engine damage, reduced efficiency, and higher emissions.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) About Different Fuel Grades
Can I mix different diesel fuel grades?
Generally, mixing different diesel fuel grades isn’t recommended. It can cause reduced engine performance due to varying cetane numbers, and fuel system issues like gelling or filter clogging, especially in cold weather. However, mixing #1 and #2 diesel, known as winterized fuel, is sometimes done to prevent gelling in cold temperatures while providing adequate lubrication and energy.
How do I know which diesel fuel grade to use for my fleet?
The ideal diesel fuel grade depends on climate and engine specifications. Use a lower number like diesel #1, to avoid gelling in cold climates. Whereas for warm weather, a higher number diesel, like #2, is usually appropriate. Also, check your vehicle or engine manual for specific fuel recommendations.
What is the highest grade diesel?
The idea of a “highest grade” diesel can be misleading, as diesel is classified by numbers (e.g., #1, #2) based on climate suitability rather than quality. However, some types of diesel have added additives for better performance or lower emissions, often labeled as “premium” or “high-performance.”
What is the difference between #1 diesel and #2 diesel fuel?
#1 diesel fuel is a lighter, more refined type, suitable for colder temperatures and often referred to as winterized diesel. In contrast, #2 diesel is heavier and more commonly used for regular diesel vehicles, offering better fuel economy in warmer conditions.
How does the cetane rating affect diesel fuel performance?
The cetane rating measures the ignition quality of diesel fuel. A higher cetane number indicates that the fuel ignites more quickly in the engine, which can lead to smoother operation, better fuel economy, and reduced emissions.
What is biodiesel fuel and how does it differ from traditional diesel?
Biodiesel fuel is made from renewable sources such as vegetable oils or animal fats, making it more environmentally friendly. Unlike traditional diesel, which is derived from petroleum, biodiesel can provide similar performance with lower emissions.
Why is winterized diesel important?
Winterized diesel is formulated to prevent fuel gelling in cold temperatures, ensuring reliable fuel delivery and preventing clogging of fuel lines and filters. This is crucial for truckers and diesel vehicles operating in colder climates.
What impact do diesel fuel additives have on performance?
Diesel fuel additives can enhance fuel quality by improving cetane ratings, preventing fuel gelling, and cleaning the fuel system. This helps reduce wear and tear on engine parts and can lead to better overall performance.
How can I choose the recommended fuel grade for my diesel vehicle?
To choose the recommended fuel grade, consult your vehicle’s owner manual. Factors such as engine type, operating conditions, and manufacturer specifications should guide your choice between 1 diesel and 2 diesel fuel or other diesel grades.
Are there any differences in fuel quality among diesel grades?
Yes, the fuel quality can vary significantly among different types of diesel fuel. Factors like cetane rating, sulfur content, and presence of fuel additives contribute to the overall quality and performance of each grade.

Fuel Logic Can Help You Select the Right Fuel Grade!
For quality diesel fuel delivery and expert advice you can count on, reach out to Fuel Logic today.
Our team can help you select the right fuel grade and provide prompt, and reliable on-site, off-road, diesel exhaust fuel and bulk diesel delivery service across 48 locations in the US.
By taking into account your engine type and climgaate conditions, we can pick the best blend for your fleet to improve its performance and longevity. So, don’t wait at fuel stations.
Contact us to order quick gasoline delivery and fuel delivery anywhere, anytime!